3D Scanning for Automotive: Applications, Hardware, & Software
3D scanning is the process of capturing three-dimensional data from an object (including shape, appearances, color, and textures) using structured light or lasers. In this article, see how Creaform’s portfolio brings 3D scanning to the automotive space.
How is 3D Scanning Used in the Automotive Industry?
Automotive companies use 3D scanning for reverse engineering, quality control, inspection, new product development; for production parts, and manufacturing tools.
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering is the process of developing a CAD model from a physical part. In the automotive space, this is typically used for legacy parts and tooling for vehicles no longer in production. Historically, this process would be accomplished through manual measurement; usually with large CMM equipment, often with hand tools as well. 3D scanning creates a digital copy of the object, allowing the measurement work to be done by software tools.

When a company needs to remanufacture a legacy part, they would simply 3D scan the part; the resulting 3D mesh containing the physical details of the part’s topology. Reverse engineering software tools convert this data into native CAD surfaces or solid bodies, driven by fully-dimensioned sketches and features. A designer then has the freedom to make aesthetic or performance-based improvements to the original design.
Quality Control and Inspection
Quality control processes measure the dimensions of manufactured parts to determine whether or not they meet the required quality criteria. Quality assurance inspection helps prevent mistakes during the manufacturing process, and ensure that customers don’t receive faulty parts. If a company wants to check the quality of a part, 3D scanned data can be used to generate a First Article Inspection (FAI) report using scanning inspection software.
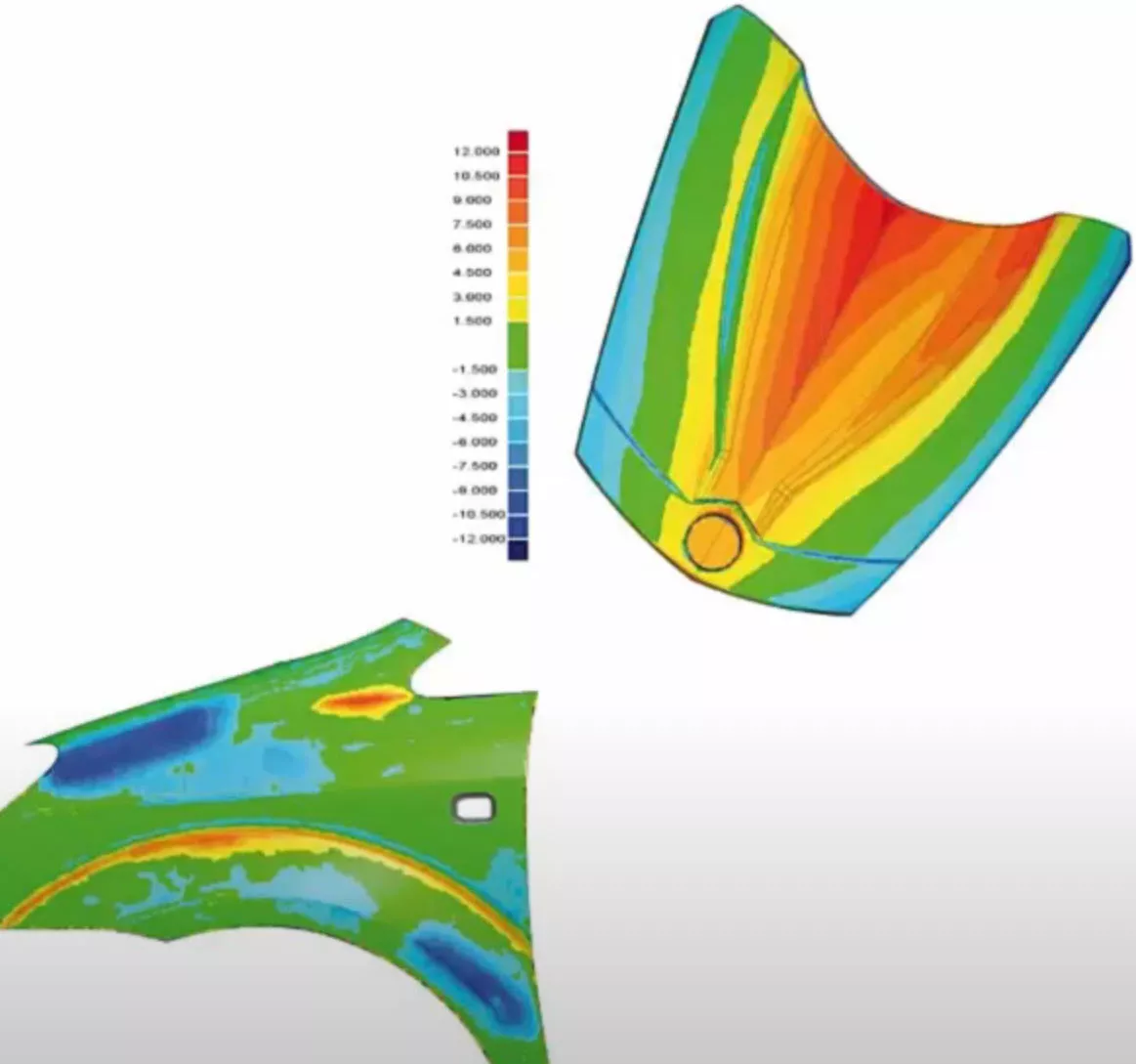
Scanned data can be used for in-process inspection as well. For example, a cut surface can be scanned in-situ (without removing the work from the CNC machine), checked for accuracy in inspection software, and corrected as needed before the operator proceeds with the next operation.
Tooling and wear-items can also be scanned for deformation analyses.The scanned data can be compared to the original CAD to see where deformations exist and used to verify the life of the tool, inform design improvement in future tools, or plan repairs if needed. Scan-to-inspection software also provides color maps and reports to help analyze the data.
New Product Development
There are many stages in the product development process. 3D scanning can be used to develop products with complex, organic shapes and geometries regardless of size. For companies that create aftermarket parts for vehicles, 3D scanned data is used to locate holes, check clearances, and match the design of a part to precisely fit a certain area of a vehicle. The scanned data can also be used to create jigs and fixtures for painting and welding processes.
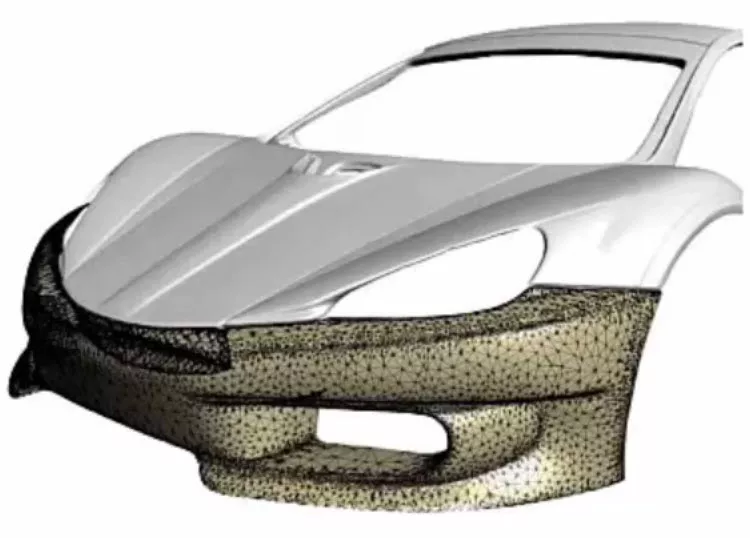

Production and Manufacturing
3D scanning is often paired with 3D printing technology for the manufacturing process. 3D printed prototypes can be produced to verify proper fit and function before a part is sent to production. Additionally, broken or damaged parts can easily be 3D scanned for 3D printed replacements.
Scan to CAD Process
The scan-to-CAD process for automotive applications contains two steps.
#1. Capture the scan data
Before you start scanning, it’s important to choose the right scanner for the job. Some 3D scanners use structured white LED lights, while others use red or red and blue laser light technology.
Factors like sunlight, dim rooms, and reflective surfaces should also be considered for optimal outcomes. Once those factors have been considered, the scanned raw data can be stored and the scanned data can be processed.
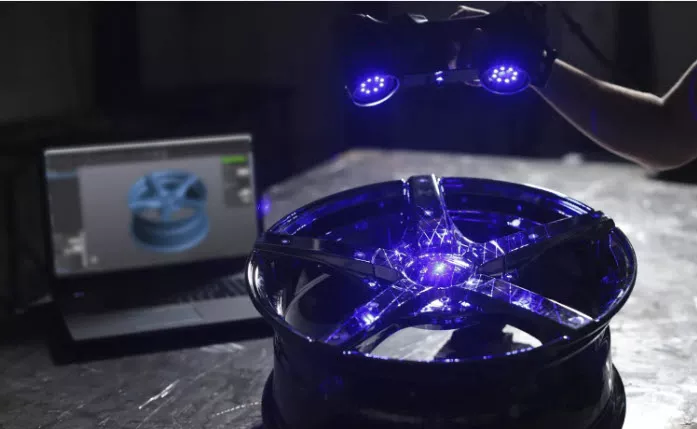

#2.Processing scanned data
In order to process scanned data, Reverse Engineering software is required to ‘clean up’ the raw data. Raw data will include unwanted areas of a part (e.g., the floor of a car) or background images picked up while scanning.
Reverse engineering software allows you to remove imperfections with smoothing tools, merge scans together, obtain reference geometry, create features (e.g., extrusions and cuts), and eventually send them to a CAD software like SOLIDWORKS.
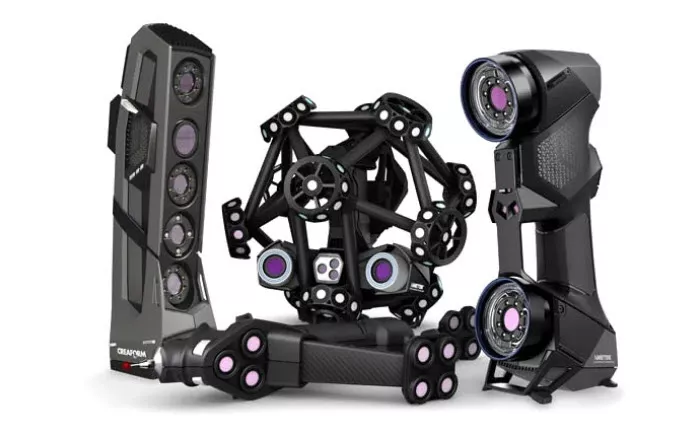
Creaform 3D Scanners For Automotive Uses
The Go!SCAN Spark (pictured left) is a powerful handheld system with outstanding accuracy and speed that uses structured white LED lights. With its seamless integration to 3D CAD software and product life cycle management workflows, the Go!SCAN is a great partner in the product development process.
The HandySCAN (pictured right) laser scanner is a handheld 3D scanner ideal for scanning parts ranging from the size of a golf ball to the size of a small car.
The MetraSCAN (pictured in the middle) is a fast and accurate handheld 3D scanner perfect for the shop floor. It uses red laser light technology to deliver accurate results, regardless of the measurement setup quality and user experience level.
(Note: View all Creafom 3D Scanners here.)
Reverse Engineering and Inspection Software
- VXmodel is a Creaform reverse engineering software that allows users to obtain reference geometry in order to recreate a part.
- Geomagic for SOLIDWORKS is a reverse engineering software that is an add-in to SOLIDWORKS so designers can do all of their reverse engineering without ever having to leave the SOLIDWORKS workspace.
- Suggested reading >> What is Geomagic for SOLIDWORKS?
- Geomagic Wrap is a reverse engineering software that has auto surfacing tools that can help clean up a mesh and get you a solid body quickly and easily.
- Geomagic Design X is the flagship software for reverse engineering. It includes full-CAD capabilities, as well as the ability to transfer features into SOLIDWORKS using a live transfer.
- Suggested Reading >> Geomagic Design X Features and Tutorials
- VXinspect (a Creaform inspection software) and Geomagic Control X inspection software allow for the creation of color maps, taking measurements, and creating full reports for an inspection.
Customer Story
Drake Automotive Group is an aftermarket automotive part company specializing in classic Ford Mustangs. They needed a technology that could give them a full 3D model of the parts they were working on. They chose the Creaform HandySCAN based on its accuracy to aid them in the product development and inspection, and because of its portability and ease of use. Learn more about their journey with 3D scanning below.
3D Scanning as a Service
GoEngineer offers professional 3D scanning services for companies looking to bring a physical model into their digital workspace. Request your quote online today!
More 3D Scanning Articles
Creaform Releases New HandySCAN 3D SILVER Series 3D Scanners
The GoEngineer Trifecta: Creaform, Geomagic & Stratasys
3D Technology and Archaeology: Enabling Artifacts to Virtually & Literally Travel the World

About GoEngineer
GoEngineer delivers software, technology, and expertise that enable companies to unlock design innovation and deliver better products faster. With more than 40 years of experience and tens of thousands of customers in high tech, medical, machine design, energy and other industries, GoEngineer provides best-in-class design solutions from SOLIDWORKS CAD, Stratasys 3D printing, Creaform & Artec 3D scanning, CAMWorks, PLM, and more
Get our wide array of technical resources delivered right to your inbox.
Unsubscribe at any time.

